前言 JDBC代表Java数据库连接。JDBC库中所包含的API通常与数据库使用于:连接到数据库创建SQL或MySQL语句,在数据库中执行SQL或MySQL,查看和修改数据库中的数据记录。
一、JDBC环境准备
普通Java项目,在lib中粘贴此包(在官网上下),版本无所谓
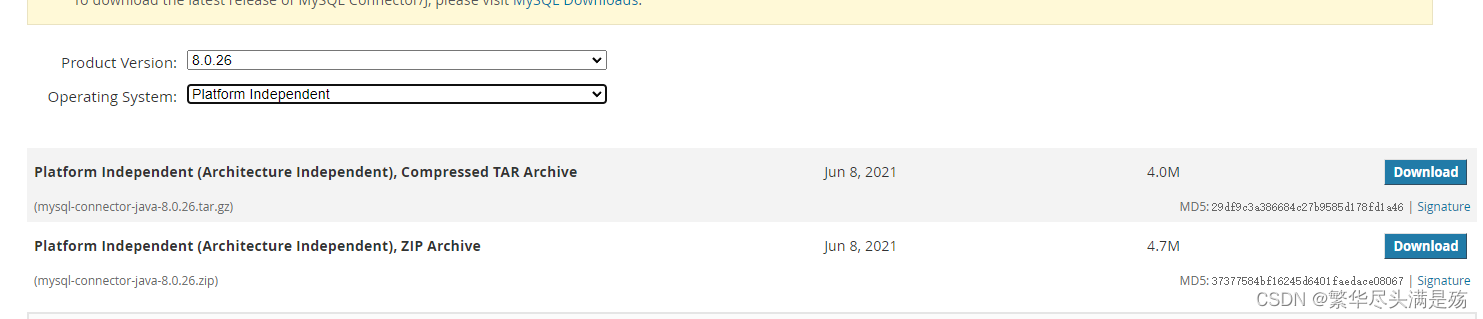
官网下载 系统选择platform那个
jar包存放位置,项目根目录下的lib文件夹
如果是Maven或者Gradle或者Spring项目。不需要引入上面的jar包,直接在依赖里面写(Maven为例)
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.31</version > </dependency >
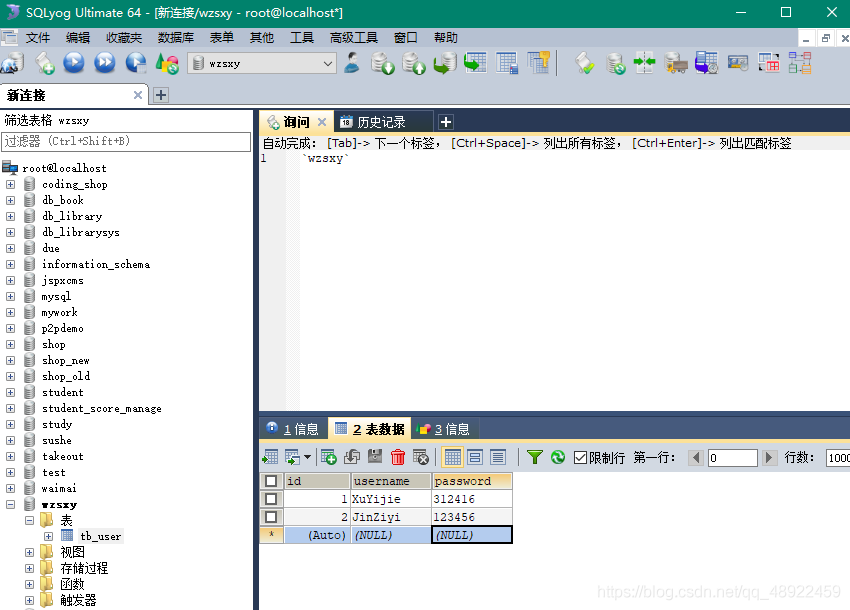
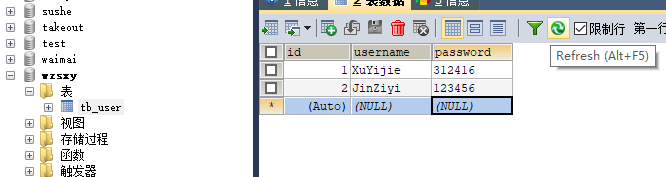
除上述环境配置外,还需要建立一个数据库,我使用的是SQLyog,假设创建一个数据库:wzsxy,在这个数据库上创建一张表:tb_user,并输入两条起始数据。如图
二、基本操作 实现数据库的查询 新建Find类
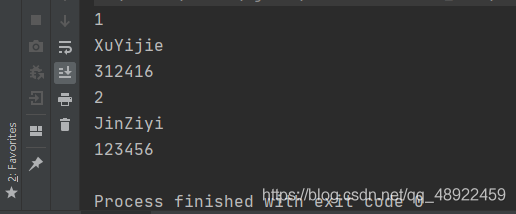
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import java.sql.*;public class Find { public static void main (String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy" ,"root" ,"123456" ); String sql="select * from tb_user" ; PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()){ System.out.println(resultSet.getInt(1 )); System.out.println(resultSet.getString(2 )); System.out.println(resultSet.getString(3 )); } resultSet.close(); statement.close(); connection.close(); } }
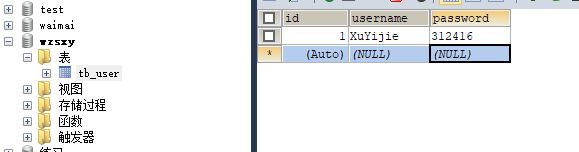
实现数据库的删除 新建Delete类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.sql.*;public class Delete { public static void main (String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy" ,"root" ,"123456" ); String sql="delete from tb_user where id=2" ; PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.executeUpdate(); statement.close(); connection.close(); } }
运行后在数据库中刷新表以后,发现id为“2”的用户被删除
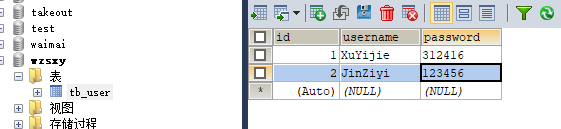
实现数据库的增添 新建Add类,在SQL语句中输入要增加的信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.sql.*;public class Add { public static void main (String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy" ,"root" ,"123456" ); String sql="INSERT INTO tb_user (username,PASSWORD) VALUES ('JinZiyi','123456')" ; PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.executeUpdate(); statement.close(); connection.close(); } }
运行打开数据库刷新,发现数据增加成功
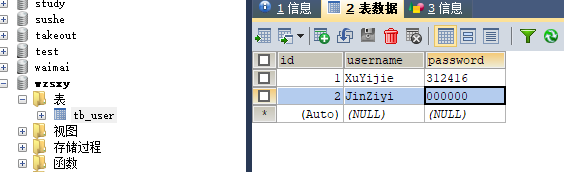
实现数据库数据的修改 新建Update类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.sql.*;public class Update { public static void main (String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy" ,"root" ,"123456" ); String sql="UPDATE tb_user SET username='JinZiyi',PASSWORD='000000' WHERE id=2" ; PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.executeUpdate(); statement.close(); connection.close(); } }
刷新数据库后可见数据修改成功
三(扩展)、整合增删改查的代码,封装为一个工具类
在util包下新建DBUtil类 将JDBC的基本步骤的1、2、7步放入DBUtil类中,代码中使用了try…catch,也可以直接idea自动生成抛出异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.XuYijie.util;import java.sql.*;public class DBUtil { public static Connection getConnection () { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Connection connection = null ; try { connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy" ,"root" ,"123456" ); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("创建连接成功" ); return connection; } public static void closeAll (ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection) throws SQLException { if (resultSet!=null ){ resultSet.close(); } if (resultSet!=null ){ statement.close(); } if (resultSet!=null ){ connection.close(); } } }
在bean包下新建User类 定义id、username、password,生成所有的get、set方法和构造方法,并重写toString
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 package com.XuYijie.bean;public class User { public User () { } private int id; private String username; private String password; public User (int id, String username, String password) { this .id = id; this .username = username; this .password = password; } public User (String username, String password) { this .username = username; this .password = password; } public int getId () { return id; } public void setId (int id) { this .id = id; } public String getUsername () { return username; } public void setUsername (String username) { this .username = username; } public String getPassword () { return password; } public void setPassword (String password) { this .password = password; } @Override public String toString () { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + '}' ; } }
在dao包下新建UserDao类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 package com.XuYijie.dao;import com.XuYijie.bean.User;import com.XuYijie.util.DBUtil;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class UserDao { public List<User> findAll () { Connection connection= null ; List<User> userList=new ArrayList <>(); PreparedStatement statement=null ; ResultSet resultSet = null ; try { connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); String sql="select * from tb_user" ; statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); resultSet = statement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()){ User user=new User (); user.setId(resultSet.getInt(1 )); user.setUsername(resultSet.getString(2 )); user.setPassword(resultSet.getString(3 )); userList.add(user); } } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { DBUtil.closeAll(resultSet,statement,connection); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } return userList; } public void deleteById (int id) { Connection connection= null ; PreparedStatement statement=null ; try { connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); System.out.println("创建连接成功" ); String sql="delete from tb_user where id=5" ; statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { DBUtil.closeAll(null ,statement,connection); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } public void add (User user) { Connection connection= null ; PreparedStatement statement=null ; try { connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); System.out.println("创建连接成功" ); String sql="INSERT INTO tb_user (username,PASSWORD) VALUES (?,?)" ; statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.setString(1 ,user.getUsername()); statement.setString(2 ,user.getPassword()); statement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { DBUtil.closeAll(null ,statement,connection); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } public void update (User user) { Connection connection= null ; PreparedStatement statement=null ; try { connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); System.out.println("创建连接成功" ); String sql="UPDATE tb_user SET username=?,PASSWORD=? WHERE id=?" ; statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); statement.setString(1 ,user.getUsername()); statement.setString(2 ,user.getPassword()); statement.setInt(3 ,user.getId()); statement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { DBUtil.closeAll(null ,statement,connection); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } }
新建Test类 Test用来实现UserDao里面的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package com.XuYijie;import com.XuYijie.bean.User;import com.XuYijie.dao.UserDao;import java.util.List;public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { UserDao userDao = new UserDao (); List<User> userList = userDao.findAll(); System.out.println(userList); userDao.deleteById(4 ); User user = new User (); user.setUsername("HeGuanghui" ); user.setPassword("123456" ); userDao.add(user); user.setUsername("HeGuanghui" ); user.setPassword("654321" ); userDao.update(user); } } }
然后就可以自己运行试试啦
结语 JDBC在现在的正规项目中已经不使用了,但是初学者仍然要了解一些,另外JDBC可以在普通项目中作为临时连接数据库的方法使用,切换方便,非常灵活。
Spring和Maven操作数据的教程可以看我的传送门,可以在网页上展示数据,有源码,非常简单易懂
Maven工程实现前后端的数据展示与操作