前言 mutations和actions都是Vuex.Store里定义函数的方法
mutations定义的函数的参数都有一个state,表示store里的整个state数据,同步加载
actions定义的函数里的参数是content,代表整个store对象,用于异步加载
先上代码在说话 便于比较,我把mutations和actions写到了一起
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > store-mutations和actions实现的计数器</title > <script src ="vue.js" > </script > <script src ="vuex.js" > </script > </head > <body > <div id ="app" > <button @click ="add" > mutations</button > <button @click ="add1" > actions</button > <p > {{count}}</p > </div > <script > var store = new Vuex .Store ({ state :{ count :0 }, mutations :{ add :function (state,value ){ state.count ++, console .log (state); console .log (value); } }, actions :{ add :function (content ){ console .log (content); this .timer = setTimeout (()=> { content.commit ("add" ) },1000 ); } } }) var a = new Vue ({ el :"#app" , store, data :{ pare :"五一劳动节" }, methods : { add :function ( this .$store .commit ("add" ,this .pare ) }, add1 :function ( this .$store .dispatch ("add" ) } }, computed :Vuex .mapState ({ count :state =>count }) }) </script > </body > </html >
解析 DOM结构是这样的
1 2 3 4 5 <div id ="app" > <button @click ="add" > mutations</button > <button @click ="add1" > actions</button > <p > {{count}}</p > </div >
两个按钮分别调用了Vue里的add和add1方法,add和add1的区别在于commit和dispatch
我还在commit里面加上了一个参数pare,这个pare是定义在Vue的data里的,值是“五一劳动节”,这个值可以传递到mutations里的add方法里,下面会介绍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 methods : { add :function ( this .$store .commit ("add" ,this .pare ) }, add1 :function ( this .$store .dispatch ("add" ) } },
commit调用的是mutations里的add方法,dispatch调用的是actions里的add方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 mutations :{ add :function (state,value ){ state.count ++, console .log (state); console .log (value); } }, actions :{ add :function (content ){ console .log (content); this .timer = setTimeout (()=> { content.commit ("add" ) },1000 ); } }
运行代码
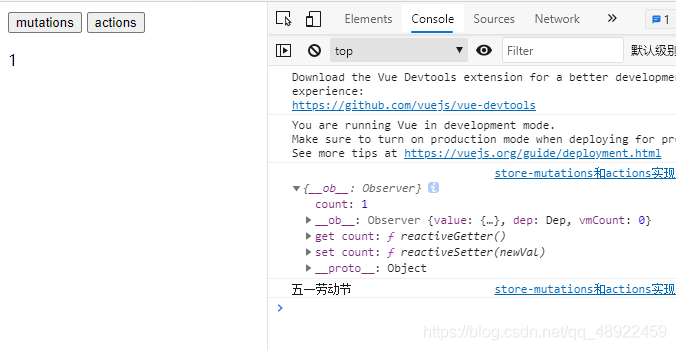
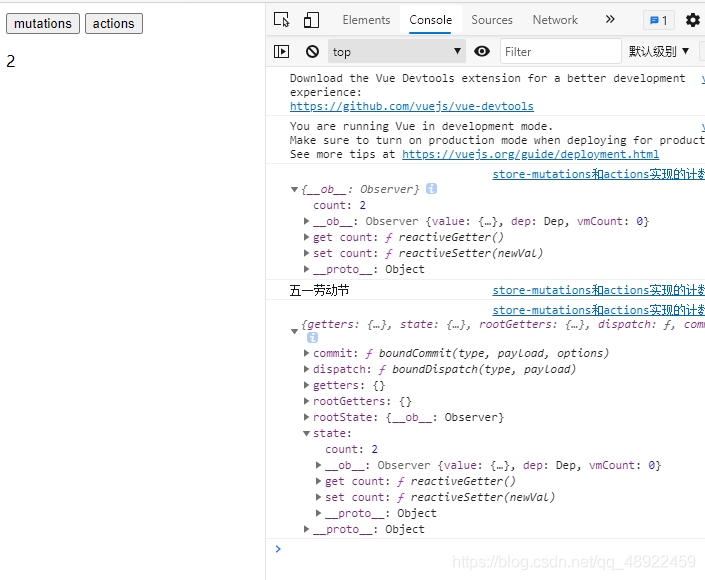
如上图,我们先点击mutations按钮,右边控制台输出了mutations里add方法的state的值和传来的pare的值
接下来我们再点击actions按钮,右边控制台输出了actions里add方法的content的值,content的值里面包含上面的state
异步加载延时计数器 看这一段代码,我们在actions的add方法里面,并没有直接使用count++来使计数加1,而是调用了mutations里的add方法来进行加1,目的就是实现异步加载,把commit(“add”)放在setTiomeout里面,代表1000毫秒以后调用mutations里的add方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 mutations :{ add :function (state,value ){ state.count ++, console .log (state); console .log (value); } }, actions :{ add :function (content ){ console .log (content); this .timer = setTimeout (()=> { content.commit ("add" ) },1000 ); } }
当然你也可以直接写成
1 2 3 4 this .timer = setTimeout (()=> { content.state .count ++ },1000 ); }